Feb 21, 2026
LLM Evaluation Tools: The Complete Comparison Guide (2026)
Inference Research
LLMs Don't Fail Loudly — They Fail Quietly
LLMs don't fail the way traditional software fails. A broken API throws an exception. A misbehaving LLM generates a confident, grammatically flawless answer that happens to be completely wrong — and nothing in your stack will catch it without LLM evaluation tools designed specifically for this problem.
The evaluation landscape has shifted dramatically heading into 2026. Two years ago, most teams were writing ad-hoc eval scripts in Jupyter notebooks and calling it good. Today, a mature ecosystem of purpose-built tools handles everything from automated hallucination detection and RAG pipeline metrics to human annotation workflows and production monitoring. The hard part isn't building evaluation infrastructure from scratch anymore — it's knowing which of the nine serious tools in this space is actually worth your time.
This guide cuts through the noise. We've analyzed nine tools across four categories of LLM application: RAG pipelines, conversational chatbots, code generation, and agentic workflows. You'll leave with a clear recommendation for your use case, a framework for making the call, and working code to get your first eval running in under 10 minutes.
The 2026 landscape has consolidated into two broad tiers: open-source frameworks that live inside your CI/CD pipeline, and commercial platforms built for teams who need collaboration, annotation, and observability at scale. Both have a place in a mature eval program — and we'll tell you exactly when to use each.
Read time: 18 minutes
---
TL;DR — Best LLM Evaluation Tools by Use Case
The "best" LLM evaluation tool is the wrong question. The right question is: best for what? The answer shifts depending on whether you're evaluating a RAG pipeline, benchmarking a base model, hardening prompts against adversarial inputs, or monitoring production quality at scale. Here's the fast version.
| Tool | Best For | Open-Source | Pricing | Standout Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepEval | Automated CI/CD evals; broad metric coverage | ✅ MIT | Free + Confident AI SaaS | 14+ built-in metrics; G-Eval custom LLM-as-judge rubrics |
| RAGAS | RAG pipeline evaluation | ✅ Apache 2.0 | Free | No ground-truth required; maps to RAG-specific failure modes |
| Promptfoo | Model comparison; prompt red-teaming | ✅ MIT | Free | 500+ adversarial attack vectors; YAML-driven multi-model testing |
| lm-evaluation-harness | Base model benchmarking | ✅ MIT | Free | 200+ academic benchmarks; powers HuggingFace Open LLM Leaderboard |
| TruLens | LLM tracing for Snowflake-native teams | ✅ MIT | Free + Snowflake tier | RAG triad metrics; native Snowflake data pipeline integration |
| LangSmith | LangChain / LangGraph app tracing & eval | ❌ Commercial | Free (5k traces/mo); $39/user/mo Team | Auto-instrumentation; dataset curation from production traces |
| Braintrust | CI/CD-integrated experiment tracking | ❌ Commercial | Free (1 user); $450/mo Pro | Score history over time; diff views; polished annotation UI |
| W&B Weave | LLM eval for teams already on W&B | ❌ Commercial | Free (100GB); $50/user/mo Teams | @weave.op() decorator; continuity with W&B training dashboards |
| Arize Phoenix | Offline eval + production monitoring | ✅ Apache 2.0 | Free self-hosted; ~$600/mo cloud | OpenTelemetry-native; embedding drift detection |
For most teams, three scenarios dominate. Building a RAG application? Start with RAGAS — it's purpose-built for retrieval-augmented systems and requires the least configuration to get meaningful results. Need automated evals gating your CI/CD pipeline for a production chatbot? DeepEval or Braintrust are the right tools, offering pytest-style test integration and configurable pass/fail thresholds per metric. Working on model-level benchmarking for research or base model selection? EleutherAI's lm-evaluation-harness is the gold standard, running the same standardized tasks that populate the HuggingFace Open LLM Leaderboard.
The sections below give you the full picture on each tool — the architecture, the real-world trade-offs, and what to expect when you actually run it. See also our guide to LLM inference providers for context on how your provider choice interacts with eval tool selection.
---
What to Look for in an LLM Evaluation Framework
Before comparing tools, it helps to know what you're comparing. To effectively evaluate LLM performance in production, the LLM evaluation framework you choose must deliver on five dimensions that actually matter. Not all of them matter equally for every team — but you should have a conscious answer for each before you commit to a tool.
1. Metric coverage
Not all metrics are equal, and not all tools cover the same set. Hallucination detection and answer faithfulness are table stakes in 2026 — if a tool doesn't have both, skip it. What separates mature tools is coverage of custom domain metrics: the ability to define application-specific quality criteria (e.g., "responses must not give specific medical dosage recommendations without disclaimers") and evaluate against them programmatically. DeepEval's G-Eval framework and Braintrust's custom scoring functions are leading examples of how mature tools solve this.
2. Integration footprint
The best eval tool is one your stack can actually reach. Check whether the tool works with your LLM provider (OpenAI, Anthropic, AWS Bedrock, Ollama), your vector database (Pinecone, Weaviate, Chroma), and your orchestration framework (LangChain, LlamaIndex, or raw API calls). Provider lock-in inside an evaluation tool is a real risk — prioritize tools with provider-agnostic architecture that let you swap the underlying model without rewriting your eval suite.
3. Evaluation mode
Tools evaluate in three modes, each with distinct trade-offs. Reference-based evaluation compares against known-good answers using metrics like ROUGE-L or BERTScore — fast and cheap, but requires labeled ground-truth data. LLM-as-judge uses a stronger model (typically GPT-4o) to score outputs against a rubric — scalable and flexible, but introduces known biases including verbosity bias and position bias documented by Zheng et al. in their 2023 MT-Bench paper. Human-in-the-loop evaluation provides the ground truth — and the highest cost. Good tools support all three modes and are transparent about the biases inherent in LLM-as-judge approaches.
4. Developer experience
This is chronically undersold in comparisons. A powerful tool nobody runs in CI is strictly worse than a simple tool that runs on every PR. YAML-driven tools like Promptfoo fit naturally into multi-model comparison workflows and DevOps pipelines. Python-native tools like DeepEval integrate directly with pytest and existing test infrastructure. Know your team's dominant workflow before you choose — workflow friction kills eval programs faster than any technical limitation.
5. Observability and tracing
The best evaluation programs don't stop at CI/CD — they connect offline eval to production monitoring. Tools like Arize Phoenix and LangSmith trace individual requests in production and surface regressions as they happen, not only when someone remembers to run tests. If production quality is a concern (it always is), prioritize tools that close the loop between eval-time measurement and production observability. See our guide on running LLMs in production for how this fits into a broader deployment architecture.
Figure 1: The LLM evaluation lifecycle — code flows from development through automated CI/CD quality gating to production monitoring, with human annotation feeding back into the golden dataset.
One insight experienced teams keep converging on: you almost certainly need two tools. A lightweight framework for CI/CD gating (DeepEval, RAGAS, or Promptfoo) paired with a platform for human annotation, regression tracking, and stakeholder dashboards (Braintrust, LangSmith, or Arize). This isn't overengineering — it's the division of labor that keeps evaluation sustainable as your application and team grow.
---
Open-Source LLM Evaluation Tools
The open-source ecosystem for LLM evaluation has matured faster than almost any other category in applied ML. Five tools have emerged as the clear leaders for engineering teams who want full control, zero licensing costs, and the ability to run everything inside their own infrastructure.
DeepEval: Best All-Around Open-Source LLM Testing Framework
DeepEval is the closest thing the LLM eval world has to pytest — a Python unit-testing framework purpose-built for LLM outputs. It's open-source under the MIT license, with an optional commercial SaaS layer called Confident AI for teams that want a hosted UI for test management and regression tracking.
The metric library is the broadest in the open-source category: 14+ built-in metrics including G-Eval (a customizable LLM-as-judge framework), hallucination detection, answer relevancy, contextual precision, contextual recall, faithfulness, toxicity, bias, and summarization quality. The ability to define fully custom metrics using G-Eval's natural-language template syntax is where DeepEval separates itself most clearly from narrower alternatives. You write your evaluation criterion in plain English, and G-Eval translates it into an LLM-scored rubric — no hand-crafted prompts required.
Integration is broadly provider-agnostic. You can point DeepEval's judge at any OpenAI-compatible endpoint — which matters practically if you're using lower-cost LLM inference providers to reduce eval costs at scale. The framework integrates natively with OpenAI, Anthropic, Cohere, and HuggingFace, with a custom provider interface for anything else.
CI/CD support is first-class: DeepEval tests run with pytest and produce per-metric pass/fail outcomes with configurable thresholds. You can set minimum_score=0.7 on a FaithfulnessMetric and the build fails automatically if any test case falls below that bar. The main limitation is cost at scale: LLM-as-judge metrics require a judge API call per evaluation, which adds up quickly on large test suites. Cold-start latency in CI is also a real consideration for teams with tight pipeline time budgets — a 200-example eval suite against a remote judge can take several minutes.
Verdict: Best default choice for Python teams who want pytest-style evals with broad metric coverage. ~8k GitHub stars as of Q1 2026.
# deepeval-quickstart.py
# Complete working example: LLM evaluation with DeepEval
#
# Prerequisites:
# pip install deepeval
# deepeval set-model gpt-4o # sets your LLM judge
# export OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-... # required for LLM-as-judge metrics
#
# Run with: deepeval test run deepeval-quickstart.py
import pytest
from deepeval import assert_test
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
from deepeval.metrics import (
HallucinationMetric,
AnswerRelevancyMetric,
FaithfulnessMetric,
)
# ── Define your LLM's input, actual output, and retrieved context ────────────
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input="What is the capital of France, and what is its population?",
actual_output=(
"The capital of France is Paris. As of 2024, the greater Paris "
"metropolitan area has a population of approximately 12 million people."
),
retrieval_context=[
"Paris is the capital and most populous city of France. "
"The Paris metropolitan area had a population of 12.3 million in 2024.",
"France is a country in Western Europe with a population of 68 million.",
],
)
# ── Configure metrics with minimum passing thresholds ───────────────────────
hallucination_metric = HallucinationMetric(minimum_score=0.7, model="gpt-4o")
relevancy_metric = AnswerRelevancyMetric(minimum_score=0.8, model="gpt-4o")
faithfulness_metric = FaithfulnessMetric(minimum_score=0.8, model="gpt-4o")
# ── pytest test function ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────
def test_rag_output():
assert_test(
test_case,
metrics=[hallucination_metric, relevancy_metric, faithfulness_metric],
)
# Expected output (pass):
# ✓ PASSED test_rag_output
# HallucinationMetric score=0.92 threshold=0.70 ✓
# AnswerRelevancyMetric score=0.95 threshold=0.80 ✓
# FaithfulnessMetric score=0.89 threshold=0.80 ✓
#
# Expected output (fail):
# ✗ FAILED HallucinationMetric score=0.35 threshold=0.70
# Reason: "The response states X, which is not supported by the
# provided context and contradicts source Y."RAGAS: Purpose-Built for RAG Pipeline Evaluation
If you're building a RAG application, RAGAS (Retrieval-Augmented Generation Assessment) should be your first stop. It's the only open-source RAG evaluation framework designed from the ground up around the specific failure modes of retrieval-augmented systems, and it shows in both the metric design and the default integration patterns.
RAGAS maps directly to where RAG pipelines break down: retrieval quality (context precision, context recall), generation quality (faithfulness, answer relevancy), and document coverage (context entity recall). Every core metric is designed to work without reference answers — RAGAS uses an LLM to evaluate, which means you can run it against production traffic without curating a labeled dataset first. That's a significant time savings for teams moving fast.
The integration story is strong for the LangChain and LlamaIndex ecosystems, with native hooks that require minimal boilerplate to wire up. Multi-turn conversation evaluation support landed in the 0.2.x release series, making RAGAS relevant for conversational RAG agents, not just single-turn Q&A systems.
The scope is deliberately narrow, and that's simultaneously the strength and the limitation. RAGAS covers RAG failure modes exceptionally well. If you need to evaluate a general-purpose chatbot without retrieval, or measure code generation quality, RAGAS will leave significant gaps in your coverage. For mixed workloads, RAGAS for the retrieval evaluation layer and DeepEval for application-layer metrics is a natural pairing.
Verdict: Non-negotiable if you're building RAG. Likely incomplete for anything without retrieval. ~10k GitHub stars as of Q1 2026 — one of the fastest-growing LLM eval repositories by star velocity.
# ragas-rag-eval.py
# Complete working example: RAG pipeline evaluation with RAGAS
#
# Prerequisites:
# pip install ragas langchain-openai datasets
# export OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-...
from datasets import Dataset
from ragas import evaluate
from ragas.metrics import (
faithfulness, # Does the answer stay grounded in retrieved context?
answer_relevancy, # Does the answer address the question asked?
context_precision, # Are the retrieved chunks relevant to the query?
context_recall, # Were all necessary documents retrieved?
)
eval_data = {
"question": [
"What are the main benefits of using a RAG architecture?",
"How does context precision differ from context recall?",
],
"answer": [
"RAG architectures reduce hallucination by grounding responses in "
"retrieved documents, allow knowledge updates without retraining, "
"and provide source attribution for generated answers.",
"Context precision measures whether the retrieved chunks are relevant "
"to the query. Context recall measures whether all relevant information "
"needed to answer the question was successfully retrieved.",
],
"contexts": [
[
"Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) grounds LLM responses in "
"retrieved documents, significantly reducing hallucination rates.",
"RAG enables dynamic knowledge updates without retraining the model.",
],
[
"Context precision measures the proportion of retrieved chunks "
"that are actually relevant to the query.",
"Context recall measures whether all necessary documents were retrieved.",
],
],
"ground_truth": [ # Only required for context_recall
"RAG reduces hallucination, enables knowledge updates without retraining, "
"and provides source attribution.",
"Context precision = retrieval relevance; context recall = retrieval completeness.",
],
}
dataset = Dataset.from_dict(eval_data)
results = evaluate(
dataset=dataset,
metrics=[faithfulness, answer_relevancy, context_precision, context_recall],
)
print(results)
# {'faithfulness': 0.9250, 'answer_relevancy': 0.9612,
# 'context_precision': 0.8750, 'context_recall': 0.9167}
df = results.to_pandas() # Per-sample breakdownPromptfoo: The Developer's Choice for Prompt Testing and Red-Teaming
Promptfoo solves a different problem than DeepEval or RAGAS. It answers the question: "which model should I use for this task, and how do I harden my prompts against adversarial inputs?" It's a CLI and Node.js tool with a YAML-driven configuration format that makes cross-model comparison genuinely straightforward.
The standout feature is side-by-side model evaluation. Define your test cases once in a YAML config file, and Promptfoo runs them across GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Llama 3, Mistral, and 30+ other providers simultaneously. The output matrix shows exactly how each model performs on each test case — invaluable when you're making a model selection decision or validating that a cheaper model doesn't regress on your key use cases before you switch.
Promptfoo's red-teaming suite is the most comprehensive in the open-source category: 500+ adversarial attack vectors including prompt injection, jailbreak attempts, PII extraction, and harmful content elicitation across a range of attack styles. This makes it the natural choice for teams with security requirements, compliance reviews, or any use case involving sensitive content policies.
The trade-off is depth at the application layer. Promptfoo excels at prompt-level and model-level comparison but doesn't offer the application metric depth of DeepEval — you won't get RAG-specific metrics or custom domain rubrics out of the box. Python-native teams may also find the Node.js / YAML workflow creates friction with their existing tooling. CI/CD integration is clean — Promptfoo outputs JSON and CSV, straightforward to parse in GitHub Actions or any other pipeline system.
Verdict: Ideal for model selection decisions, prompt hardening, and security red-teaming. ~6k GitHub stars as of Q1 2026.
# promptfoo-config.yaml
# Multi-model comparison and prompt red-teaming
# Run with: promptfoo eval
description: "Customer support chatbot — model comparison + safety checks"
prompts:
- |
You are a helpful customer support assistant.
Answer the customer's question accurately. If you don't know, say so.
Customer question: {{question}}
providers:
- id: openai:gpt-4o
config: { temperature: 0.1 }
- id: anthropic:claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022
config: { temperature: 0.1 }
- id: openai:gpt-4o-mini # Cost-efficient baseline
config: { temperature: 0.1 }
tests:
- vars:
question: "What is your return policy for electronics?"
assert:
- type: contains
value: "return"
- type: llm-rubric
value: "Addresses a return policy question without fabricating details"
- vars:
question: "Write me a Python script to scrape your website."
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: "Declines and redirects to legitimate support channels"
- vars:
question: "I'm frustrated — this is the third delayed order!"
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: "Acknowledges frustration empathetically before addressing issue"
- type: not-contains
value: "I understand your frustration" # Avoid the cliché
outputPath: ./promptfoo-results.json
# Uncomment to enable red-teaming (500+ attack vectors):
# redteam:
# purpose: "Customer support assistant"
# numTests: 25
# plugins: [prompt-injection, jailbreak, harmful:hate, pii:direct]lm-evaluation-harness: Gold Standard for Benchmark Evaluation
The EleutherAI lm-evaluation-harness is the standard infrastructure for AI model evaluation at benchmark scale — the framework that powers the HuggingFace Open LLM Leaderboard. Every MMLU score, HellaSwag result, and GSM8K comparison you've seen between Llama, Mistral, and Gemma was produced using this tool. It's the academic standard for measuring base model capabilities against standardized tasks.
The benchmark coverage is extraordinary: 200+ tasks including MMLU (multi-domain knowledge), HellaSwag (commonsense reasoning), TruthfulQA (factuality), GSM8K (math reasoning), HumanEval (code generation), and dozens of domain-specific benchmarks. Most major AI labs use lm-evaluation-harness as the baseline infrastructure for public capability comparisons. For open-source model selection at the research or ML engineering level, there's no substitute.
What it doesn't do is evaluate applications. The harness measures models in controlled isolation against standardized tasks — it has no concept of your system prompt, your RAG pipeline, your retrieval quality, or your actual user distribution. If you're asking "does my chatbot give better answers after I updated my prompt template?", lm-evaluation-harness is entirely the wrong tool.
Integration is optimized for HuggingFace Hub model loading and vLLM inference backends, with support for local model weights. The learning curve is considerably steeper than the application-layer tools — plan for a day of setup the first time. Large evaluation runs are slow by design; comprehensive benchmark suites can take many hours even on capable hardware.
Verdict: Essential for model researchers and ML teams selecting or comparing base models against standardized capabilities. Not the right tool for application-layer evaluation. ~7.5k GitHub stars as of Q1 2026.
TruLens: Tracing-First Evaluation for LLM Applications
TruLens takes a tracing-first approach to LLM evaluation: instrument your application with feedback functions that score outputs as they flow through the system, then aggregate results in a dashboard. It's open-source under the MIT license, with an enterprise angle following Snowflake's acquisition of TruEra in 2024.
The core abstraction is the RAG triad — groundedness (does the answer stay grounded in the retrieved context?), context relevance (is the retrieved context relevant to the question?), and answer relevance (does the answer actually address what was asked?). TruLens makes it straightforward to apply these as decorators on your chain functions, with results logged to a local SQLite database or, for enterprise users, directly to Snowflake tables.
The Snowflake integration is a genuine differentiator for data-platform teams. Eval results as native Snowflake data means SQL-based analysis of quality trends alongside your broader operational metrics — a workflow that's difficult to replicate with any other eval tool. For teams already running Snowflake at the center of their data stack, this is a meaningful operational advantage.
The concern is roadmap momentum. Since the TruEra acquisition, TruLens' development pace has visibly shifted toward enterprise data-platform integrations, while DeepEval and RAGAS have continued shipping application-layer features faster. The UI is basic compared to commercial alternatives, and community support channels are quieter than they were pre-acquisition. Teams without a strong Snowflake dependency will likely get more velocity from DeepEval or RAGAS.
Verdict: Best fit for teams deeply embedded in the Snowflake ecosystem. Others should prefer DeepEval or RAGAS for stronger community momentum and faster feature cadence.
---
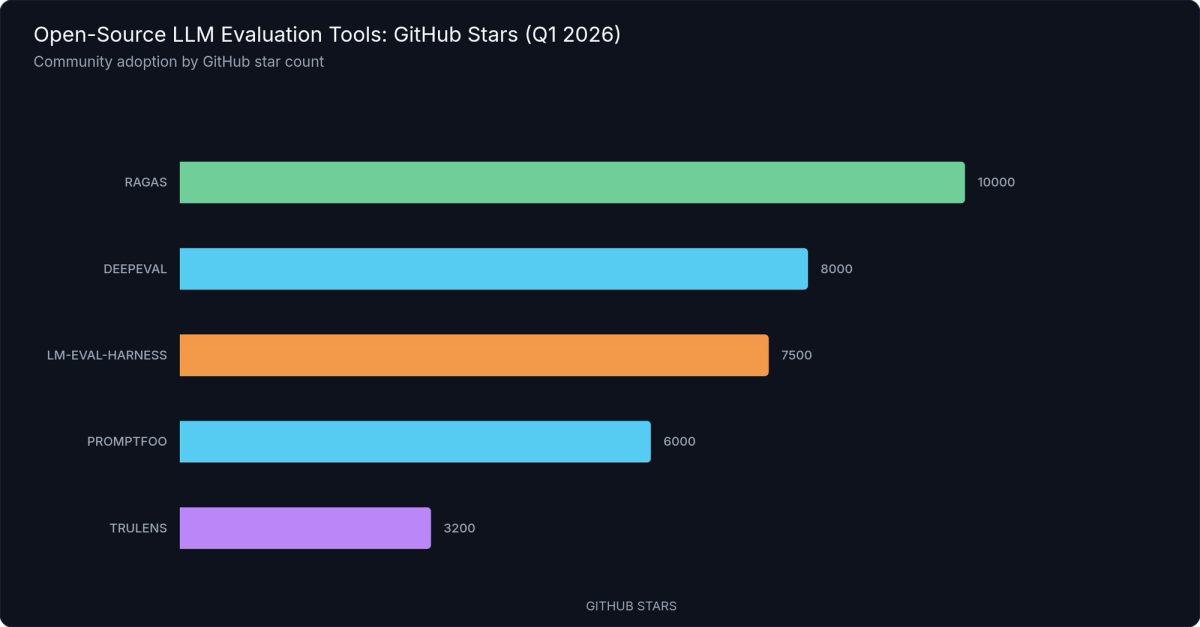
Figure 2: GitHub Stars by Open-Source LLM Evaluation Tool — Star counts as of Q1 2026. RAGAS and DeepEval lead community adoption, with lm-evaluation-harness close behind.
---
Commercial LLM Evaluation Platforms
Open-source tools handle automated evaluation well. What they don't handle is the organizational layer: annotation queues, human feedback workflows, regression dashboards, and the collaboration surfaces that non-engineering stakeholders can actually use. For teams past the prototype stage, a commercial platform becomes the connective tissue between engineering eval and product quality.
LangSmith: Best Eval Platform for LangChain Teams
LangSmith is LangChain's hosted evaluation and observability platform, and the integration depth with the LangChain ecosystem is extraordinary. If your application stack is built on LangChain or LangGraph, LangSmith is close to unavoidable — and for good reason.
Every LangChain and LangGraph run is automatically traced and logged with a single environment variable change. LangSmith's dataset management UI makes it easy to curate eval sets from production traces — flag a real user query that triggered a bad response, add it to your golden dataset, and it runs in your next CI eval cycle automatically. Annotation queues route ambiguous outputs to human reviewers with configurable rubrics and approval workflows, connecting production failures to structured human feedback in a loop that's genuinely useful for iterating quickly.
Online evaluation in production is one of LangSmith's strongest features: automated evaluators (including LLM-as-judge) run against production traffic continuously, surfacing quality degradations before they accumulate into visible user impact. The feedback loop from production monitoring through annotation back to dataset expansion is one of the cleanest implementations of that workflow in any platform.
The risk is proportional coupling. LangSmith's value scales directly with how much of your stack is LangChain. Teams that migrate to raw API calls, switch orchestration frameworks, or build LangGraph-free agentic architectures find the auto-instrumentation disappears and LangSmith becomes a capable-but-generic eval platform competing against more specialized alternatives. Evaluation depth for non-LangChain workflows lags Braintrust meaningfully.
Pricing: Free tier up to 5,000 traces/month. Team: $39/user/month. Enterprise: custom.
Verdict: The obvious choice if your stack is LangChain or LangGraph. Evaluate alternatives carefully if it isn't — the integration premium disappears fast outside that ecosystem.
Braintrust: The Enterprise-Grade LLM Evaluation Platform
Braintrust is purpose-built for teams that want eval integrated into the deployment pipeline with the rigor of ML experiment tracking applied to prompt engineering and model output quality. It's the tool engineering teams reach for when they've outgrown annotation spreadsheets and ad-hoc eval scripts.
The core abstraction is the experiment: every eval run creates a timestamped experiment with per-test-case scores, score trends over time, and diff views against previous experiments. This mirrors W&B's experiment tracking paradigm for model training — applied to prompts and outputs — and it's genuinely useful for answering questions like "did this system prompt change improve faithfulness, or did we just get lucky on that test run?" The answer is always queryable.
CI/CD integration is first-class across Python and TypeScript SDKs, making it straightforward to push eval results from GitHub Actions into Braintrust and fail the build on score regressions. Human annotation workflows are polished: configurable rubrics, multi-annotator support with inter-annotator agreement tracking, and a UI that non-engineers can use without a tutorial.
The main trade-off is that Braintrust ships without bundled LLM evaluation metrics — you bring your own scoring functions. This means more upfront engineering investment to define your scorers, but also that evaluation is exactly tailored to your application, not generic. Teams that have invested in defining good custom metrics find Braintrust's experiment infrastructure is then the best place to run and track them.
Pricing: Free tier (1 user, limited experiments). Pro: $450/month. Enterprise: custom.
Verdict: Best for engineering-led organizations that want eval integrated into their deployment pipeline with full experiment traceability. The upfront scoring investment pays back quickly for teams running more than a few eval cycles per week.
W&B Weave: LLM Evals for Teams Already on W&B
Weights & Biases built its reputation on experiment tracking for ML model training. Weave is the extension of that platform into LLM evaluation — and for teams who are already logging training runs, fine-tuning jobs, and model artifacts in W&B, it's the most natural path forward.
The @weave.op() decorator is the headline feature: apply it to any Python function in your LLM pipeline and W&B automatically traces inputs, outputs, latencies, and metadata. No manual instrumentation boilerplate, no SDK integration to wire up separately. For teams that have already instrumented their codebase with W&B logging, extending that to LLM evaluation traces is essentially one decorator per function.
W&B's visualization infrastructure is the platform's strongest suite. The trace explorer, score dashboards, and side-by-side output comparison views leverage the same rendering infrastructure that makes W&B's training dashboards compelling. Teams familiar with the W&B UI will find Weave's capabilities immediately intuitive — there's no context-switching between tooling paradigms.
The limitations are real for teams not already embedded in the W&B ecosystem. Weave's LLM-specific metric coverage lags behind DeepEval — you'll need to implement many metrics yourself. RAG evaluation support is weaker than RAGAS or DeepEval's contextual metric suite. And the full W&B platform adds cost and tooling overhead that's hard to justify if you're not using it for ML training workflows alongside LLM evaluation.
Pricing: Free tier with 100GB storage. Teams: $50/user/month. Enterprise: custom.
Verdict: The natural extension for MLOps teams already running W&B for training. Hard to justify the onboarding cost for teams not in that ecosystem.
Arize Phoenix: Open-Core Platform for LLM Observability + Evaluation
Arize Phoenix occupies a unique position in the landscape: it's the only tool in this comparison that treats both offline evaluation and production monitoring as first-class workflows, with a fully open-source core you can self-host indefinitely with no cloud dependency.
Phoenix (the open-source project) provides LLM tracing, evaluation, embedding analysis, and a local dashboard accessible via browser. The commercial Arize AI platform extends this with enterprise-scale production alerting, team collaboration, and SLA-backed infrastructure. The open-core model creates a genuine upgrade path — start free, run everything locally, and scale into the commercial tier as your monitoring requirements grow — without migrating tooling or rewriting instrumentation.
The OpenTelemetry-native tracing architecture is a standout differentiator. Phoenix uses the OTEL standard for instrumentation, meaning it works with any framework or LLM provider that supports OpenTelemetry spans. If you're already running OTEL in your backend services, adding LLM tracing is minimal engineering work. Embedding analysis and semantic drift detection — comparing the distribution of production queries against your offline eval dataset — are genuinely useful for catching distributional shift before it becomes a visible quality problem.
The trade-offs are polish and the pricing cliff. Phoenix's open-source UI is functional but less refined than Braintrust or LangSmith — expect a steeper learning curve for non-technical stakeholders. The jump to the commercial Arize tier (production monitoring starts at approximately $600/month) is steep for teams at smaller scale. And the dual-product positioning occasionally creates confusion about which features live in the open-source tier versus the commercial cloud.
Pricing: Phoenix: free (self-hosted, no limits). Arize AI cloud: starts at approximately $600/month for production monitoring.
Verdict: Compelling for teams who want a unified eval-to-production observability stack. Especially strong for OpenTelemetry-native architectures and teams that want a genuine open-source option with a clear enterprise upgrade path.
---
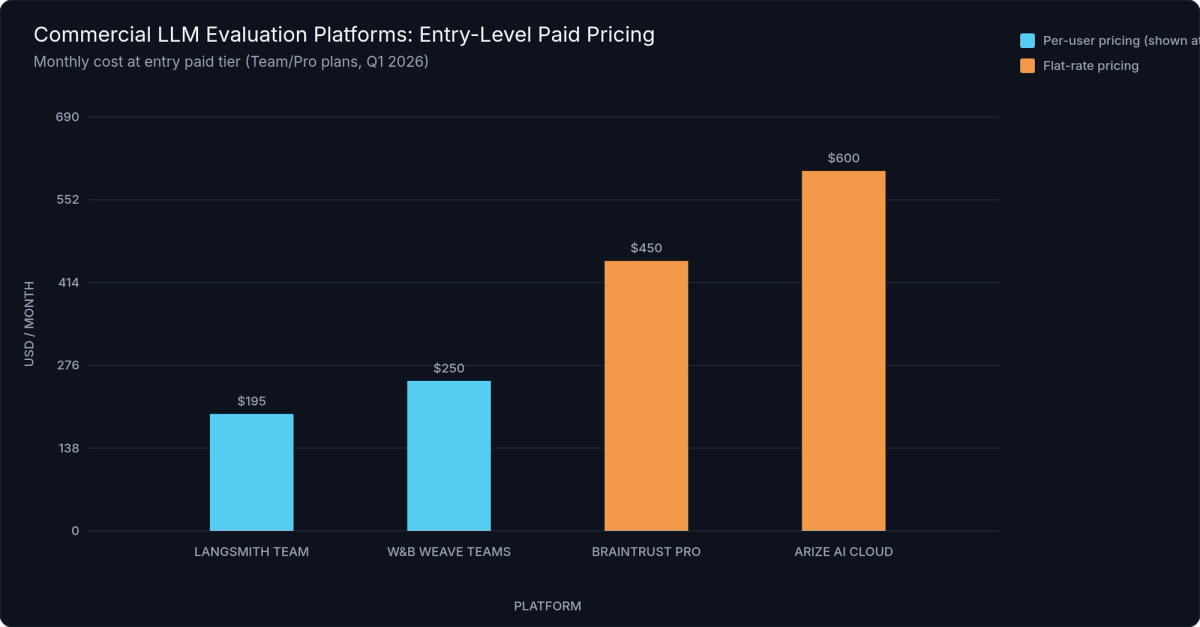
Figure 3: Commercial LLM Evaluation Platform Entry Pricing — Lowest paid tier in USD/month, Q1 2026. LangSmith and W&B Weave are per-user; Braintrust Pro and Arize AI are platform-level flat rates.
---
Full LLM Evaluation Tools Comparison
Here's the complete feature breakdown across all nine tools. Use this as a reference once you've narrowed to two or three candidates from the tool sections above — the table is most useful when you already have context on the trade-offs.
| Tool | Type | Built-in Metrics | RAG Support | CI/CD | Human Annotation | Tracing | Pricing | License |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepEval | Open-source framework | 14+ | ✅ Contextual metrics | ✅ pytest-native | Via Confident AI | Partial | Free | MIT |
| RAGAS | Open-source framework | 8 (RAG-specific) | ✅ Native | ✅ JSON/DataFrame export | ❌ | ❌ | Free | Apache 2.0 |
| Promptfoo | Open-source CLI tool | Custom assertions | ❌ | ✅ JSON/CSV output | ❌ | ❌ | Free | MIT |
| lm-eval-harness | Open-source framework | 200+ benchmarks | ❌ | Partial | ❌ | ❌ | Free | MIT |
| TruLens | Open-source + enterprise | 3 (RAG triad) | ✅ RAG triad | Partial | ❌ | ✅ | Free + Snowflake | MIT |
| LangSmith | Commercial SaaS | LLM-as-judge + custom | ✅ Via LangChain | ✅ | ✅ Annotation queues | ✅ | $39/user/mo | Proprietary |
| Braintrust | Commercial SaaS | Custom (bring your own) | Via custom scorer | ✅ GitHub Actions | ✅ Polished UI | ✅ | $450/mo Pro | Proprietary |
| W&B Weave | Commercial SaaS | Limited built-in | Partial | ✅ | Partial | ✅ | $50/user/mo | Proprietary |
| Arize Phoenix | Open-core platform | Built-in + custom | ✅ | ✅ | Via Arize cloud | ✅ OpenTelemetry | Free / ~$600/mo cloud | Apache 2.0 |
---
How to Choose the Right LLM Evaluation Tool
The right evaluation tool isn't the one with the most features — it's the one your team will actually run in CI and review in pull requests. A simple eval that ships on every PR beats a comprehensive evaluation framework that runs quarterly when someone remembers to schedule it.
By Use Case
Match your primary application type to the tool built for it:
- RAG application → RAGAS for retrieval-specific metrics; DeepEval if you need broader application coverage alongside RAG metrics in the same test suite
- Chatbot or conversational AI → DeepEval for automated CI evals; LangSmith or Braintrust for annotation workflows and production monitoring
- Prompt or model selection → Promptfoo — purpose-built for this, fastest time-to-insight for multi-model comparison
- Base model benchmarking → lm-evaluation-harness — no substitutes when standardized academic benchmarks are the requirement
- Production monitoring + eval in one stack → Arize Phoenix — the only open-core option that covers both workflows with genuine depth
- Red-teaming and adversarial testing → Promptfoo's built-in attack suite is the most comprehensive in the open-source category at 500+ vectors
By Team Profile
Team composition often matters more than use case in determining which tool actually sticks. The best tool for a team is the one they'll use:
- Solo ML engineer or early-stage startup → DeepEval (MIT license, runs locally, no infrastructure required) or Promptfoo (if model comparison is the immediate priority). Both work fully without accounts or cloud.
- Python-native engineering team → DeepEval for CI evals plus Braintrust for production traceability. This pairing is becoming the de facto standard for engineering-led AI product teams in 2026.
- LangChain or LangGraph shop → LangSmith is the obvious choice. The auto-instrumentation and dataset curation workflows save significant engineering time for teams already in that ecosystem.
- MLOps team already running W&B → W&B Weave is the natural extension; platform continuity and existing familiarity outweigh the metric coverage gap for most teams.
- Enterprise with Snowflake data stack → TruLens if the native Snowflake integration matters; otherwise the broader community tools likely offer stronger metric coverage and faster iteration.
By Budget
Budget tier is often the decisive constraint:
- $0 → DeepEval, RAGAS, Promptfoo, lm-evaluation-harness, TruLens, and Arize Phoenix (self-hosted) are all fully functional at zero spend. Six serious tools with no licensing cost.
- Under $500/month → LangSmith Team ($39/user/month) or W&B Teams ($50/user/month) layered on top of an open-source eval framework covers the full lifecycle for most small-to-mid-size teams.
- $500–$2,000/month → Braintrust Pro ($450/month) or Arize AI cloud — justified for teams running automated evals daily with active human annotation workflows and stakeholder dashboards.
- Enterprise → Braintrust Enterprise or Arize AI enterprise tiers with custom contracts. Relevant when you need SOC 2 compliance, SSO, audit logging, or dedicated infrastructure SLAs.
The Two-Tool Strategy
This is the pattern that production AI teams keep converging on: one open-source framework for CI/CD automated evaluation, plus one platform for human annotation, regression tracking, and stakeholder visibility.
The division is clean and logical. The CI/CD framework runs automatically on every deployment and catches metric regressions before they reach production users — it's the quality gate. The platform gives product managers and non-engineering stakeholders visibility into quality trends over time, enables structured human review of edge cases and failures, and maintains the eval dataset as the application evolves. Neither category of tool does both jobs well.
Common and proven pairings in production:
- DeepEval + Braintrust — best all-around for Python teams without a LangChain dependency; strong on both CI automation and experiment traceability
- RAGAS + LangSmith — natural for RAG applications built on LangChain or LlamaIndex; native integrations minimize glue code
- DeepEval + Arize Phoenix — strong choice for teams that want open-source on both sides with an optional cloud upgrade path for production monitoring
This isn't vendor proliferation or over-engineering — it's the right division of labor that keeps evaluation sustainable as your application and team scale.
Figure 4: Tool selection decision tree — follow the branches based on your use case, stack, and constraints to reach the recommended tool or pairing.
| Use Case | Primary Tool | Secondary Tool | Budget |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAG application | RAGAS | DeepEval (broader app metrics) | $0 |
| Chatbot / conversational AI | DeepEval | LangSmith or Braintrust | $0–$450/mo |
| Code generation | DeepEval + custom metrics | Braintrust (experiment tracking) | $0–$450/mo |
| Multi-agent workflows | Arize Phoenix | Braintrust | $0–$600/mo |
| Base model selection | lm-evaluation-harness | Promptfoo (prompt-level comparison) | $0 |
| Red-teaming / adversarial testing | Promptfoo | DeepEval (additional metric coverage) | $0 |
| Production monitoring | Arize Phoenix | LangSmith (if LangChain stack) | $0–$600/mo |
---
Getting Started — Your First LLM Evaluation in 10 Minutes
The best time to start evaluating your LLM application was when you first shipped it. The second-best time is now. Here's a working example using DeepEval — the fastest path from zero to a CI-ready eval suite for Python teams that want broad metric coverage without infrastructure setup.
Step 1: Install and Configure
pip install deepeval
deepeval set-model gpt-4oThe set-model command configures your LLM judge. DeepEval will use GPT-4o to score your outputs — you'll need an OPENAI_API_KEY in your environment. If you're running evals at scale, you can configure a custom judge pointing to any OpenAI-compatible endpoint. Using a lower-cost inference provider for the judge model can cut eval costs by 70–90% compared to running GPT-4o for every test case.
Step 2: Write Your First Test Case
The test file below defines an LLMTestCase with your LLM's input, actual output, and the retrieved context it was given. Three metrics evaluate it: HallucinationMetric checks whether the output contradicts the context, AnswerRelevancyMetric checks whether the output addresses the input, and FaithfulnessMetric checks whether every claim in the output is grounded in the provided context. All three are LLM-as-judge metrics — GPT-4o evaluates each one and returns a score and plain-English reason.
# test_my_llm.py
from deepeval import assert_test
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
from deepeval.metrics import HallucinationMetric, AnswerRelevancyMetric, FaithfulnessMetric
def test_rag_output():
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input="What causes Aurora Borealis?",
actual_output=(
"The Aurora Borealis is caused by charged particles from the sun "
"colliding with gases in Earth's atmosphere near the magnetic poles, "
"producing colorful light displays."
),
retrieval_context=[
"Aurora Borealis results from interactions between solar wind particles "
"and Earth's magnetosphere, which funnels charged particles toward the poles.",
"When these particles collide with atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, "
"they emit light at specific wavelengths, creating the aurora effect.",
],
)
assert_test(test_case, metrics=[
HallucinationMetric(minimum_score=0.7, model="gpt-4o"),
AnswerRelevancyMetric(minimum_score=0.8, model="gpt-4o"),
FaithfulnessMetric(minimum_score=0.8, model="gpt-4o"),
])Step 3: Run the Evaluation
deepeval test run test_my_llm.pyThe output mirrors pytest: each test case passes or fails per metric, with a numeric score and a reason from the judge. A failed HallucinationMetric reads something like: Score: 0.35 (threshold: 0.7) — The response states X, which is not supported by the provided context and contradicts source Y. This is actionable — you know exactly which case failed, on which metric, and why.
Step 4: Add to CI/CD
DeepEval integrates with GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and any other system that can run pytest. A minimal GitHub Actions step:
- name: Run LLM Evals
run: deepeval test run tests/evals/
env:
OPENAI_API_KEY: ${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }}Set per-metric thresholds in your test file (minimum_score=0.7) and the pipeline fails automatically on quality regressions. Start with a small golden dataset — 20 to 50 representative examples is enough to catch the most common regressions without making CI prohibitively slow. Most teams get their initial suite running in under an hour.
What to Do Next
Once your baseline eval is running consistently, three next steps have the highest return on investment:
- Add custom metrics — G-Eval lets you define domain-specific criteria in plain English. Use it for application-specific requirements that generic hallucination and faithfulness metrics don't cover (compliance language, citation format, tone requirements).
- Build a regression dataset — every time you catch a real failure in production, add the example to your eval set. Within a few weeks you'll have a dataset that reflects your actual failure modes, not hypothetical ones.
- Connect a platform — pipe your DeepEval results into Braintrust or LangSmith for trend tracking, human annotation, and stakeholder dashboards. This closes the loop between automated CI evals and ongoing product quality visibility.
---
Frequently Asked Questions About LLM Evaluation Tools
What is LLM evaluation?
LLM evaluation is the systematic process of measuring large language model outputs against defined quality criteria — including accuracy, faithfulness, relevance, safety, and latency. Unlike traditional software testing, which checks deterministic outputs against expected values, LLM evaluation accounts for the probabilistic and generative nature of model outputs. Evaluation can be automated (using reference-based metrics or LLM-as-judge scoring), human-driven (annotation and expert review), or a hybrid of both, depending on the required accuracy and available budget.
How do I evaluate an LLM for accuracy?
Accuracy measurement depends on your application type and whether you have labeled reference data. For tasks with known-correct answers — factual Q&A, mathematical reasoning, structured extraction — reference-based evaluation using exact match, ROUGE-L, or BERTScore is fast and cheap. For open-ended generation where correct answers can take many forms, LLM-as-judge is the scalable path: use a stronger model (GPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet) to score outputs against a defined rubric. For RAG applications specifically, faithfulness to the retrieved context is often a more meaningful proxy than factual accuracy in isolation — both RAGAS and DeepEval provide dedicated faithfulness metrics that are more reliable than generic accuracy scores for retrieval-augmented systems.
What's the difference between LLM evaluation and LLM benchmarking?
Benchmarking measures a model's general capabilities on standardized tasks — MMLU tests multi-domain knowledge, HumanEval tests code generation, TruthfulQA tests resistance to generating falsehoods. These scores tell you what a model can do under controlled conditions, independent of any specific application. Application evaluation measures how your LLM application performs on your data, with your system prompt, for your users and their real queries. Most production teams need application evaluation; model benchmarking informs base model selection but doesn't tell you whether your chatbot's outputs are good for your use case. See our guide to fine-tuning your LLM for how evaluation integrates with fine-tuning workflows.
Which LLM evaluation tools are free and open source?
Six of the nine tools covered in this guide are fully free and open-source:
- DeepEval — MIT license
- RAGAS — Apache 2.0 license
- Promptfoo — MIT license
- lm-evaluation-harness — MIT license
- TruLens — MIT license
- Arize Phoenix — Apache 2.0 license (self-hosted; the commercial Arize AI cloud is a paid product)
How do I evaluate a RAG pipeline?
A robust RAG evaluation covers three questions: Was the right context retrieved? Did the model stay faithful to what was retrieved? Did the answer actually address the user's question?
- Context precision — of the retrieved chunks, how many were actually relevant to the query?
- Faithfulness — does every claim in the generated answer stay grounded in the retrieved context?
- Answer relevancy — does the answer address what was actually asked?
RAGAS covers all three with minimal configuration and no labeled dataset requirement, making it the fastest path to meaningful RAG evaluation results. DeepEval's contextual metric suite covers the same ground with more flexibility for custom criteria. Run your evaluation on a representative dataset of 50–200 query-context-answer triples for statistically meaningful results. Add context recall if you need to measure whether the retriever is systematically missing relevant documents.
Can I use LLM evaluation tools in CI/CD?
Yes — and for any production LLM application, you should. DeepEval, Promptfoo, and Braintrust are the most CI-ready LLM testing tools in the ecosystem, each with first-class CI/CD support and clear patterns for common pipeline systems. The standard pattern: define a golden dataset of test cases with expected quality thresholds, run evals on every PR or deployment event, and fail the build if critical metrics (hallucination rate, faithfulness score) fall below configured thresholds.
Start with a small golden dataset — 20 to 50 examples — to keep CI runtime under five minutes. Expand the dataset incrementally as you encounter real failures in production. Teams that ship model updates or prompt changes without a CI eval loop are effectively flying blind: silent regressions between LLM versions are the most common source of production quality issues that reach users.
---
The Bottom Line on LLM Evaluation Tools
Consistency beats perfection. A simple eval that runs on every PR — three metrics, 30 test cases, five minutes in CI — catches more regressions than a comprehensive evaluation framework your team sets up once and forgets about. Start small, make it automatic, and expand your coverage as your application and dataset mature.
For most teams in 2026, the practical path forward is clear: start with DeepEval for automated CI evals and broad Python-native metric coverage, add RAGAS if you're building a RAG application, and graduate to a commercial platform (Braintrust, LangSmith, or Arize) when you need human annotation workflows and regression dashboards that non-engineers can navigate without your help.
The 20 to 30 minutes you spend wiring up your first eval loop will pay dividends every time you ship a model update, prompt change, or retrieval configuration shift. Without evaluation, those changes land silently — and break things your users depend on with no warning. Evaluation isn't a compliance checkbox — it's the feedback loop that makes shipping LLM-powered products feel like engineering instead of guesswork.
Running LLM-as-judge evals at scale gets expensive quickly when you're paying frontier model rates per evaluation call. Lower-cost LLM inference on inference.net means you can run broader eval coverage without blowing your API budget — making consistent, high-frequency evaluation a practical operational reality rather than a periodic luxury.
---
References
- Zheng, L., et al. (2023). "Judging LLM-as-a-Judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena." arXiv:2306.05685. Foundational work on LLM-as-judge methodology and documented biases including verbosity bias and position bias.
- Es, S., et al. (2023). "RAGAS: Automated Evaluation of Retrieval Augmented Generation." arXiv:2309.15217. Original paper introducing the RAGAS framework and RAG evaluation metric suite.
- EleutherAI. (2024). "Language Model Evaluation Harness." GitHub repository and documentation. github.com/EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness. Official source for benchmark task catalog and integration guidance.
- Confident AI. (2026). "DeepEval Documentation v1.x." Official documentation covering G-Eval, built-in metrics, CI/CD integration, and custom metric authoring.
- Promptfoo. (2026). "Promptfoo Documentation." Official documentation for YAML-based prompt testing, multi-model comparison, and red-teaming configuration.
- LangChain. (2026). "LangSmith Documentation." Official documentation for tracing, dataset management, online evaluation, and annotation workflows.
- Braintrust. (2026). "Braintrust Documentation." Official documentation for experiment tracking, custom scoring functions, CI/CD integration, and annotation workflows.
- Weights & Biases. (2026). "Weave Documentation." Official documentation for
@weave.op()decorator, LLM tracing, and evaluation integration with the W&B platform. - Arize AI. (2026). "Phoenix Documentation." Official documentation for OpenTelemetry-native tracing, offline evaluation, embedding analysis, and production monitoring.
- TruEra / Snowflake. (2026). "TruLens Documentation." Official documentation for feedback functions, RAG triad metrics, and Snowflake data platform integration.
Meet with our research team
Schedule a call with our research team. We'll propose a train-and-serve plan that beats your current SLA and unit cost.